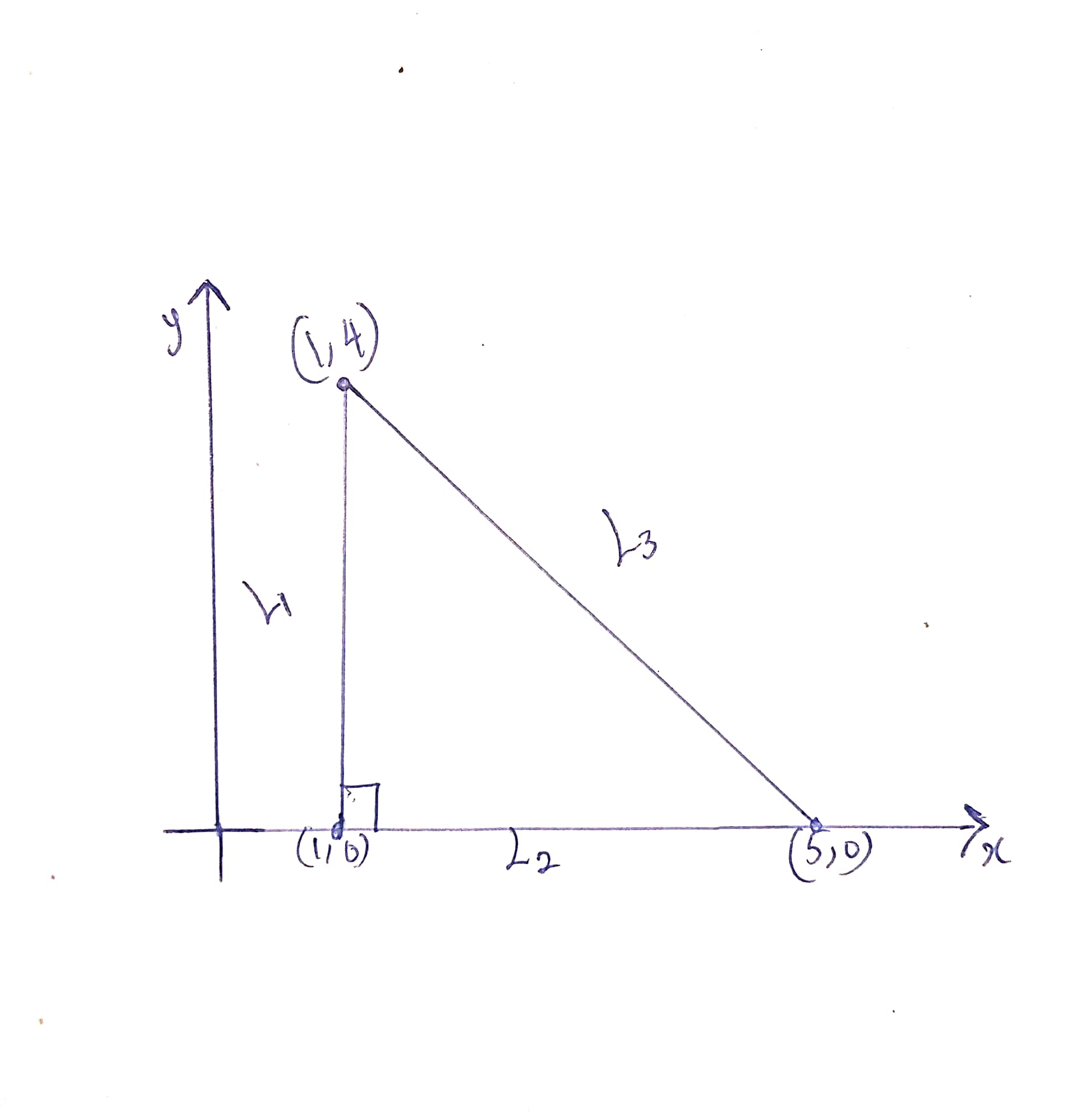
Sincefis a polynomial, it is continuous on the closed,bounded setT,whereTis the region in the triangle.The first order partial derivatives arefx(x,y)=y−1andfy(x,y)=x−2Thus, the only critical points in the interior ofTis(2,1)The boundary ofTconsists of three line segments,L1,L2andL3.OnL1,we havex=1,f(1,y)=3+y−1−2y=2−yThe functionfis a decreasing function ofyalongL1from(1,0)to(1,4)Its maximum value isf(1,0)and its minimum value isf(1,4)OnL2,we havey=0,f(1,y)=3−xThe functionfis a decreasing function ofxalongL2from(1,0)to(5,0)Its maximum value isf(1,0)and its minimum value isf(5,0)Deriving an equation for lineL3The equation can be derivedfrom the formula for the equationof a straight line passing throughone point with a gradient which is given byx−x1y−y1=m(x−x1)since the line is passing through(1,4)and(5,0)m=5−10−4=4−4=−1x−5y−0=−1∴y=5−xf(x,5−x)=3+x(5−x−1)−2(5−x)f(x,5−x)=3+4x−x2−10+2x=6x−x2−7fx(x,5−x)=6−2x=0,⟹x=3and so,(3,2)is a critical point.The values of the function at thecritical points is given by;f(3,2)f(1,0)f(5,0)f(1,4)f(2,1)=3+3(2−1)−2(3)=0=3−1=2=3−5=−2=3+1(4−1)−2(4)=−2=3+2(1−1)−2(1)=1We can hence conclude that−2is the absolute minimum of the functionf(x,y)=3+x(y−1)−2yon the closedtriangular region with vertices(1,0),(5,0)and(1,4).


Comments